Test Method
High voltage test DC

The high-voltage test DC (direct voltage) serves for testing the electric insulation capability and voltage proof of clearance and leakage paths at electric components, modules, machines, devices and systems according to various national and international regulations.
If the standard allows it, the high-voltage test DC can be used as an alternative to the high-voltage test AC. In this case, the test voltage is normally 1.5 times higher than the test voltage at AC. Either the maximum current or the minimum insulation resistance can be evaluated.
The level of the test voltage, the duration of the test, the type of test and the maximum allowed leakage current are determined in the standards.
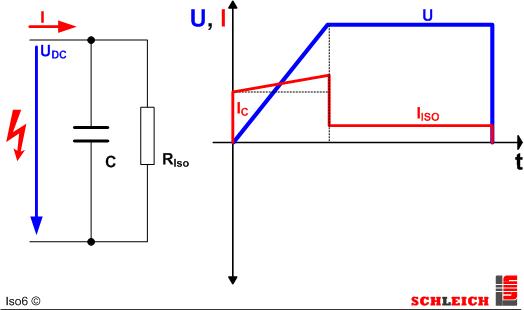
When testing with DC, this has the advantage that, similar to the insulation-resistance test, after a charging time of the capacitors, only the ohmic insulation resistance can be detected.
At the high-voltage test, the flowing test current must never be higher than a certain limit value. If this limit value is exceeded, the test voltage will be switched off immediately and automatically.
It is also possible to pre-set a minimum current. Especially in case of test objects, where a capacitive charging current is flowing at the high-voltage, it is possible to pre-set a minimum current. As soon as the minimum current is flowing, you can be sure that the test object is connected to high-voltage. Upon switching on the high-voltage test DC, the capacity in the test object is charged for a short time. This charging current impulse can be detected and serves as limit value pre-setting.
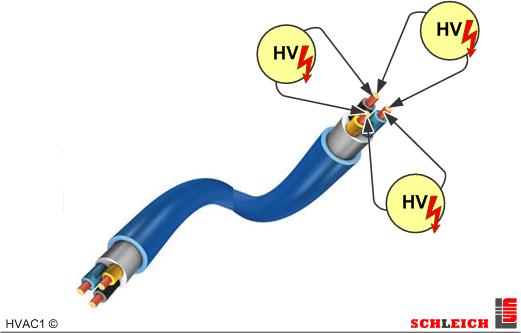
High-voltage tests are often performed at various test points by contacting the test points manually with high-voltage test pistols.
It is also possible to set up fully-automatic testers with extensive matrixes (switch-over fields) for the automatic testig at several HV test points. There is almost no limitation for the amount of matrix points.
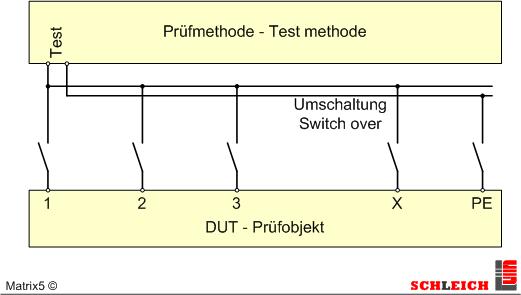
Easy switchover to test from different test points against a central test point, e.g. for testing PE.
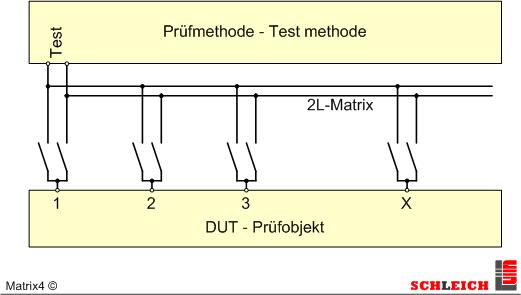
2-wire matrix, to test any test points “anyone against anyone”.
Which testers does SCHLEICH supply?
- single testers
- combination testers (combination with safety tests)
- Manual tests via test pistols
- fully automatic tests
- matrixes with up to 500 clamps and fully-automatic switchover
- testers with automatic ramp
- testers with 100 KV AC
- testers with 100 KV DC
- DC high-voltage modules
- test pistols
- various tester classes
Standard committees
For legal reasons, in many cases, we cannot make an obligatory statement about the test conditions. Important for the application is the currently valid standard for your product to be tested.
Depending on the geographical location of the product, the standards to be applied can vary. For further information, please refer to the following institutes.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

