
Check your motor's health!
Dynamic motor analysis allows you to check your running motor in its working environment. The Dynamic MotorAnalyzer measures the electrical parameters and can calculate mechanical parameters from these measurements.
With the Dynamic MotorAnalyzer you can check the mains supply, internal conditions and load conditions of your motor. An analysis of the entire electric motor is performed based only on the 6 electrical measured values (3 x U, 3 x I).
As a supplement to the MotorAnalyzer1, MotorAnalyzer2 R2 and the MTC2 winding testers, the Dynamic MotorAnalyzer completes your test device portfolio.



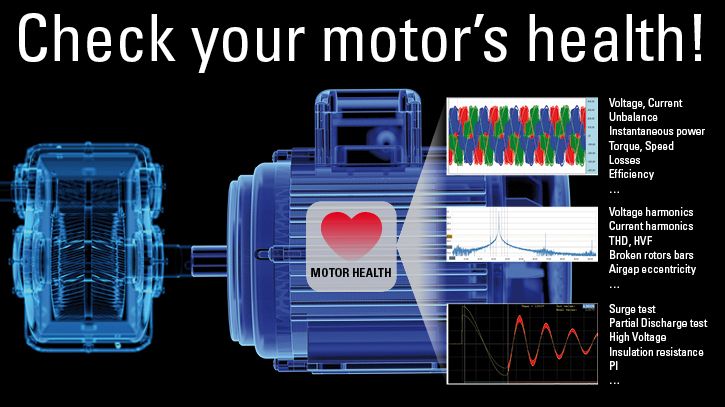
The dynamic motor analysis allows the inspection of a running motor in its working environment. For this, the electrical parameters of mains supply and motor are measured and, among others, the corresponding mechanical parameters are calculated. The aim is to receive an analysis of the electric motor, its mains supply and its load conditions – only based on 6 electrical measured values ( 3x voltage and 3x current).
The Dynamic MotorAnalyzer significantly simplifies the motor inspection- without requiring special knowledge or skills from the operator. It is the perfect supplement to our SCHLEICH- winding testers MotorAnalyzer2 and MTC2.
It often occurs that motors are operated under overload conditions or fail due to unknown reasons. This may be due to the mains supply, the motor itself or its load. The error may result from electrical or mechanical reasons.
It is often hard to detect the error cause as motors are often part of a complex plant or as it is installed in plants with difficult access.
In most cases the motor lead in the motor´s control cabinet is easier to access. Here is the perfect place to measure the 6 electrical values (3x U and 3x I). By means of a variety of analyzing methods the Dynamic MotorAnalyzer evaluates the motor´s condition. It is also possible to speak about the motor´s „health condition“.
This makes the Dynamic MotorAnalyzer an easy-to-use measuring tool for detecting complex problems within the machine´s system. Basically it is always better to determine the origin error cause before repairing or exchanging the motor. In case the problems are not properly detected the electric motor is likely to fail again. This would cause even more downtime- and repair costs, which should be avoided in any case.
The Dynamic MotorAnalyzer not only supports you in finding typical erros, but also in finding those ones which are rather difficult to detect and then to solve the problem afterwards. For this, it uses the latest methods and technologies regarding MCSA (MCSA – Motor Current Signature Analysis).
Some examples for typical errors:
Motor failures and associated machine down times may be reduced by preventive maintenance. For this, inspections of electric motors are carried out in regular intervals. The Dynamic Motoranalyzer stores all test results, evaluates them and presents them as trend analysis. Based on the graphical and easily understandable trend development you can easily find out, if a motor´s condition is getting worse and avoid downtimes by purposeful maintenance.
A perfect supplement to the Dynamic MotorAnalyzer´s test results is the ombination with the test results of the electric motor testers MotorAnalyzer2 or surge voltage tester MTC2. The test results from the motor testers may be saved together with the Dynamic MotorAnalyzer´s test results in one data base and jointly evaluated for the trend analysis. Based on the combination of test methods, you receive an even deeper look in your electric motor´s condition or technical installations.
Your production´s availability and efficiency may be increased, as downtimes can cause costs of more than hundreds of thousands Euros per hour!
Thus, the aim of preventive maintenance is to avoid interruptions and unplanned downtimes.
⇒ Find more details under Downloads.
Für weitergehende Informationen steht Ihnen unser technischer Vertrieb auch gerne telefonisch zur Verfügung.
