Know How
HV-DC Voltage Types
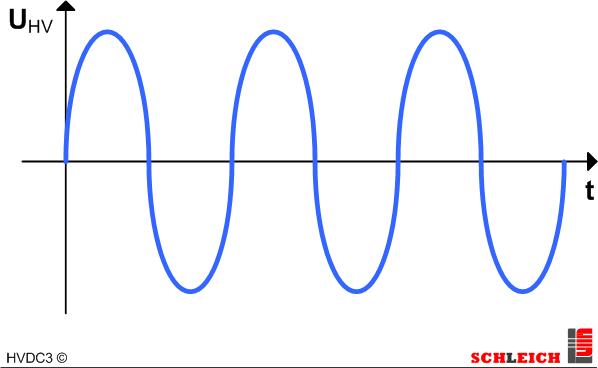
The voltage is either transformed from the mains via a high-voltage transformer or generated synthetically via an electronic source. At a transformation from the mains the sine-shape of the voltage is strongly shaped by the sine-shape of the mains. At the electronic source there is a very straight sine-wave and a very low distortion factor, as the voltage is generated, checked and controlled via a signal processor.
AC – directly from the mains
The voltage is either transformed from the mains via a high-voltage transformer or generated synthetically via an electronic source. At a transformation from the mains the sine-shape of the voltage is strongly shaped by the sine-shape of the mains. At the electronic source there is a very straight sine-wave and a very low distortion factor, as the voltage is generated, checked and controlled via a signal processor.
DC – half-wave rectification
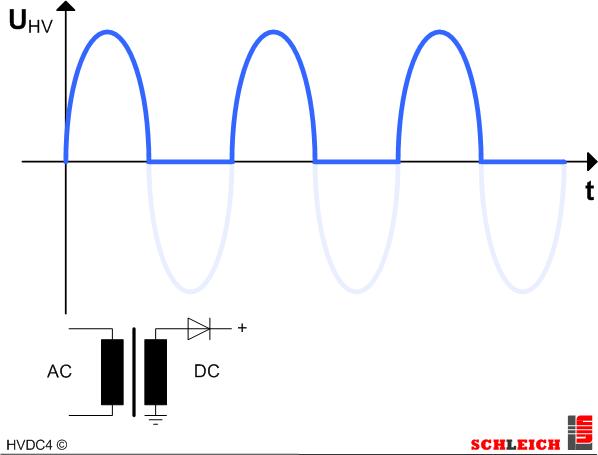
The high-voltage AC is rectified by a half-wave rectification. Thus a pulsing DC voltage occurs. This method is not expensive but has a very high ripple quality. In case the test object has a capacitive behavior, which is mainly the case, relatively much charging current thus flows into the capacity of the test object. Thus it is better to use the bridge rectification.
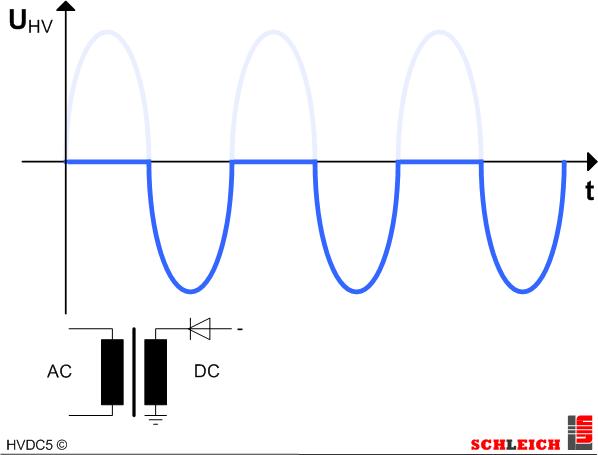
DC – bridge rectification
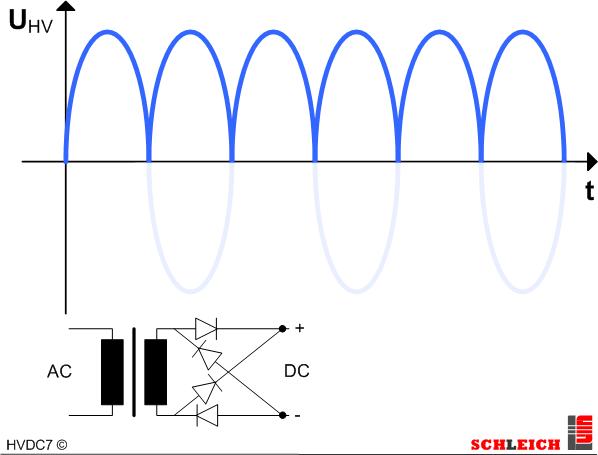
The high-voltage AC is rectified by a bridge rectification. Thus a pulsing DC voltage occurs. Compared to the half-wave rectification this method has a clearly lower ripple quality. In case the test object has a capacitive behavior, which is mainly the case, the capacitor of the test object serves as additional filter capacitor (see following picture).
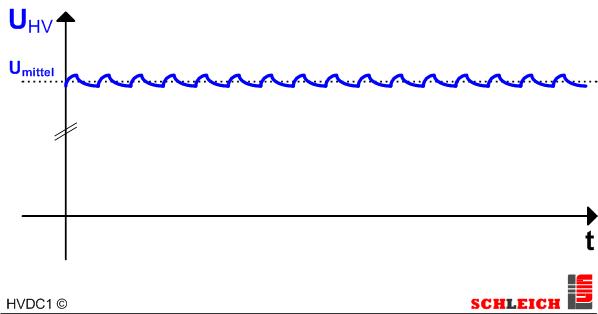
DC – bridge rectification with filter
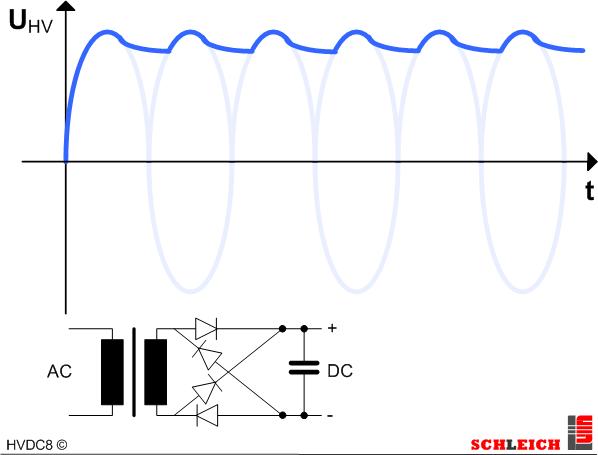
The rectified high-voltage is smoothed via an additional capacitor. The ripple quality is again reduced considerably. Hence the charging current within the capacity of the test object is also considerably reduced. Nevertheless the insulation resistance of a test object cannot be well determined with a 50Hz (60Hz) rectification with filter. To improve the ripple quality the filter capacitor could, of course, be increased considerably. But the disadvantage of this solution is a clear deterioration of the control rate. The charge and especially the discharge of the filter capacitor takes a lot of time and is responsible for a very slow high-voltage source.
Only the following version with a high frequency (for example 15KHz) and a filter brings a low ripple quality at a good control possibility of the voltage. Due to the high frequency this version only needs a small filter capacitor. It is high dynamic when adjusting the load alternations and very precise. Unfortunately this optimum high-voltage source is also the most expensive version. Voltage profiles can also be generated ideally with this version.
DC – high frequency generator with filter